Early diagnosis and treatment may improve long-term outcomes in PAH1-3
- The goal of PAH treatment is to achieve a low-risk status2
- A risk assessment should be performed at diagnosis and follow-up2
- A low-risk status at diagnosis focuses on WHO FC I or II, 6MWD >440 m, BNP <50 ng/L, NT-proBNP <300 ng/L, RAP <8 mmHg, CI ≥2.5 L/min/m2, SVI >38 mL/m2, and SvO2 >65%*
- A low-risk status at follow-up includes WHO FC I or II, 6MWD >440 m, BNP <50 ng/L, and NT-proBNP <300 ng/L
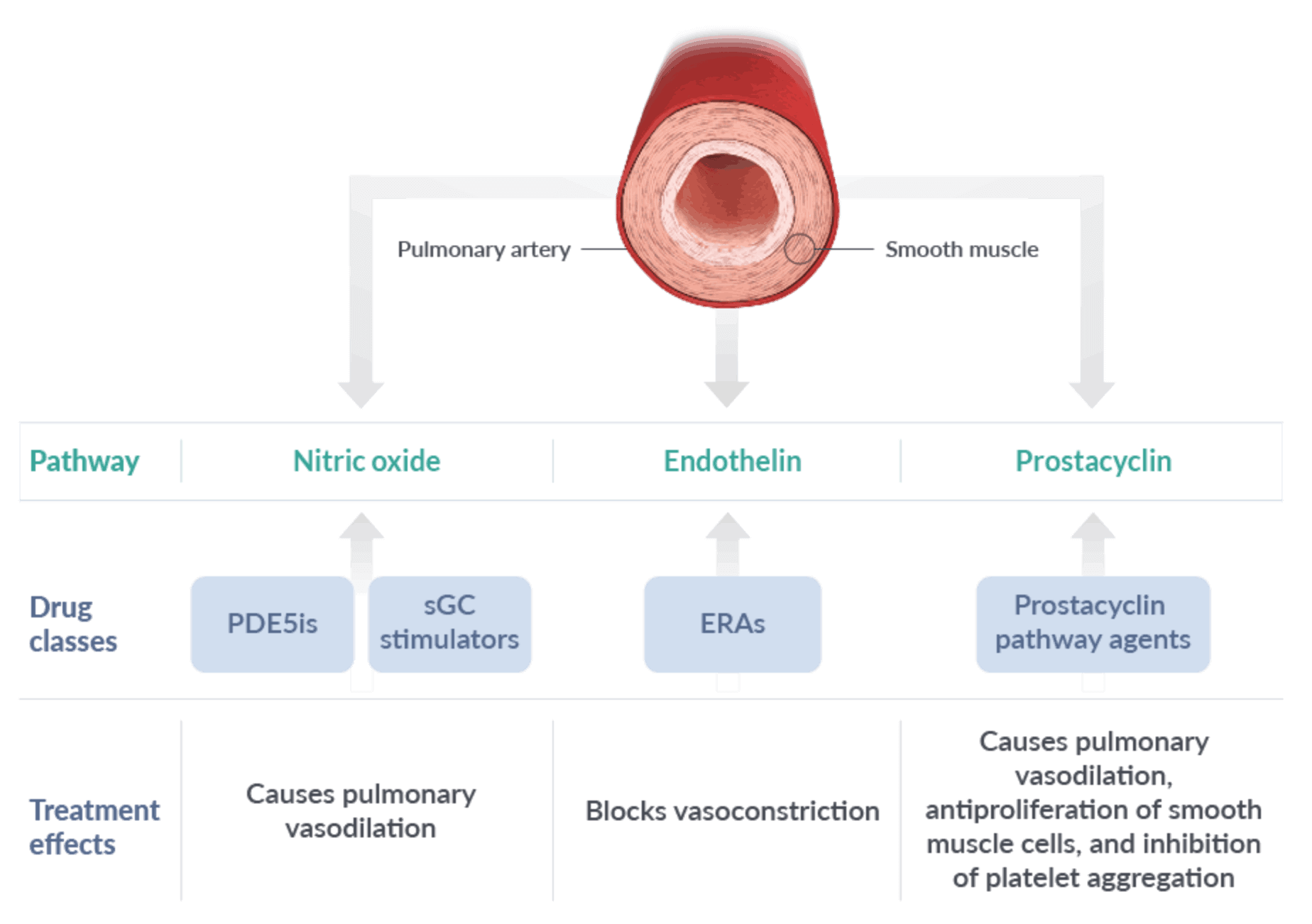
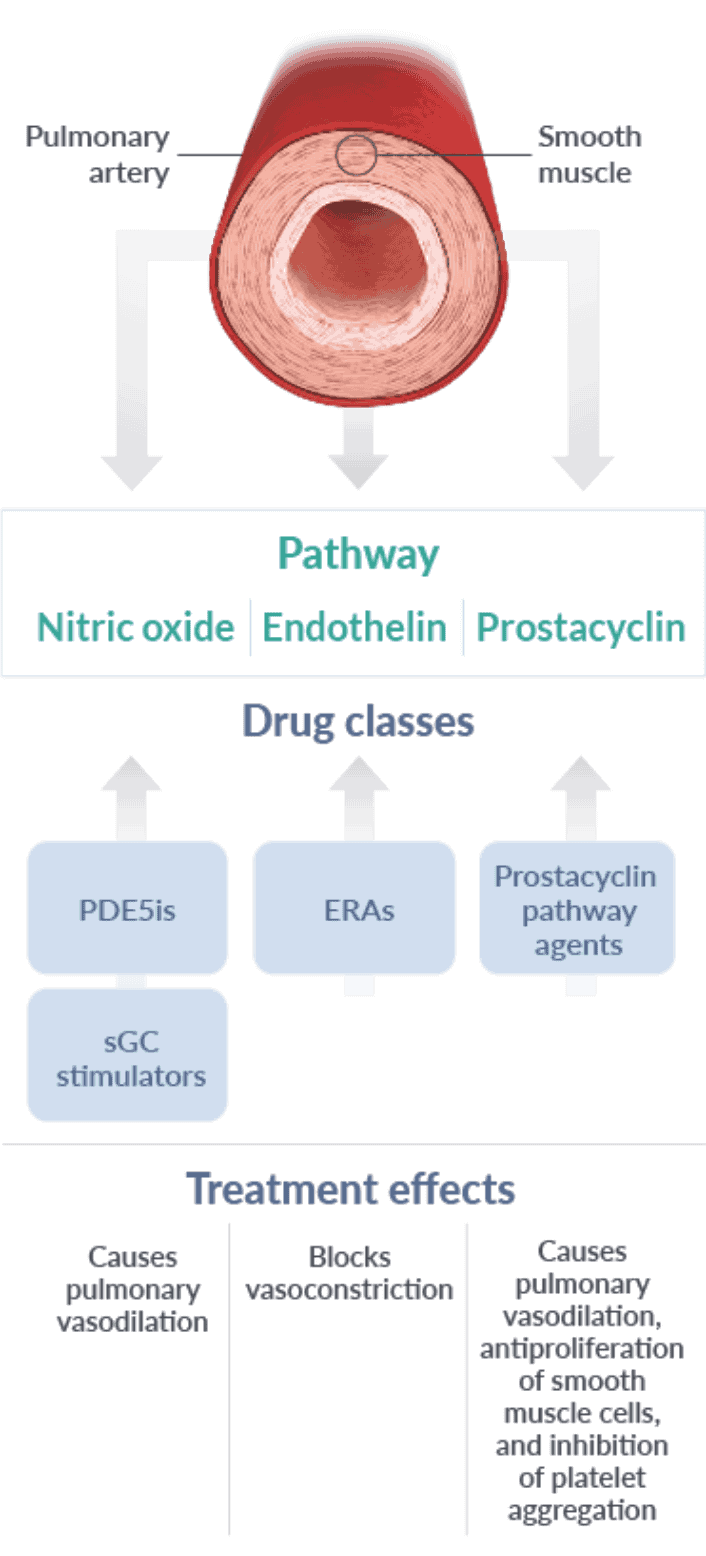
Guidelines recognize that focusing on multiple pathways is an effective treatment strategy2
- The 3 foundational signaling pathways in PAH can be targeted by different drug classes2,4:
- Nitric oxide pathway (PDE5is and sGC stimulators)2,4
- Endothelin pathway (ERAs)2,4
- Prostacyclin pathway (prostacyclin pathway agents)2,4